|
Tau
Tau (; uppercase Τ, lowercase τ or \boldsymbol\tau; ) is the nineteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless alveolar plosive, voiceless dental or alveolar plosive . In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 300. The name in English is pronounced or , but in modern Greek, Greek it is . This is because the pronunciation of the combination of Greek letters αυ can have the pronunciation of either , or , depending on what follows and if a Diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis is present on the second vowel (see Greek orthography). Tau was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter taw (𐤕). Letters that arose from tau include Roman T and Cyrillic Te (Cyrillic), Te (Т, т). Modern usage The lower-case letter τ is used as a symbol for: * Per unit tax, Specific tax amount Biology * The expressed period of the Free-running sleep, freerunning rhythm of an animal, i.e., the length of the daily cycle of an animal when kept in const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
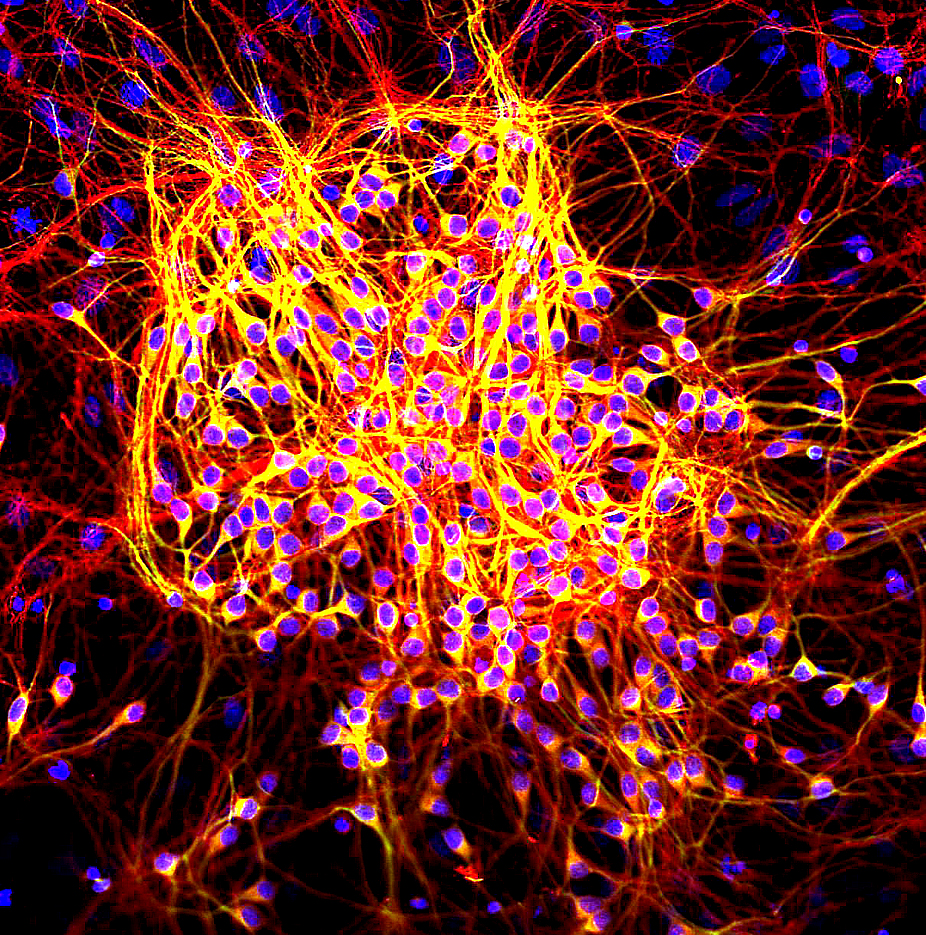
Tau (protein)
The tau proteins (abbreviated from tubulin associated unit) form a group of six highly soluble protein isoforms produced by alternative splicing from the gene ''MAPT'' (microtubule-associated protein tau). They have roles primarily in maintaining the stability of microtubules in axons and are abundant in the neurons of the central nervous system (CNS), where the cerebral cortex has the highest abundance. They are less common elsewhere but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Pathologies and dementias of the nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are associated with tau proteins that have become hyperphosphorylated insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles. The tau proteins were identified in 1975 as heat-stable proteins essential for microtubule assembly, and since then they have been characterized as intrinsically disordered proteins. Function Microtubule stabilization Tau proteins are found m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau (mathematical Constant)
The number (; spelled out as tau) is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its radius. It is approximately equal to 6.28 and exactly equal to 2Pi, . and are both circle constants relating the circumference of a circle to its linear dimension: the radius in the case of ; the diameter in the case of . While is used almost exclusively in mainstream mathematical education and practice, it has been proposed, most notably by Michael Hartl in 2010, that should be used instead. Hartl and other proponents argue that is the more natural circle constant and its use leads to conceptually simpler and more intuitive mathematical notation. Critics have responded that the benefits of using over are trivial and that given the ubiquity and historical significance of a change is unlikely to occur. The proposal did not initially gain widespread acceptance in the mathematical community, but awareness of has become more widespread, having been added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau (particle)
The tau (), also called the tau lepton, tau particle or tauon, is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with negative electric charge and a spin-1/2, spin of . Like the electron, the muon, and the three neutrinos, the tau is a lepton, and like all elementary particles with half-integer spin, the tau has a corresponding antiparticle of opposite charge but equal mass and spin. In the tau's case, this is the "antitau" (also called the ''positive tau''). Tau particles are denoted by the symbol and the antitaus by . Tau leptons have a lifetime of and a mass of /''c''2 (compared to /''c''2 for muons and /''c''2 for electrons). Since their interactions are very similar to those of the electron, a tau can be thought of as a ''much'' heavier version of the electron. Because of their greater mass, tau particles do not emit as much bremsstrahlung, bremsstrahlung (braking radiation) as electrons; consequently they are potentially much more highly penetrating than electrons. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramanujan Tau Function
The Ramanujan tau function, studied by , is the function \tau : \mathbb\to\mathbb defined by the following identity: :\sum_\tau(n)q^n=q\prod_\left(1-q^n\right)^ = q\phi(q)^ = \eta(z)^=\Delta(z), where q=\exp(2\pi iz) with \mathrm(z)>0, \phi is the Euler function, \eta is the Dedekind eta function, and the function \Delta(z) is a holomorphic cusp form of weight 12 and level 1, known as the discriminant modular form (some authors, notably Apostol, write \Delta/(2\pi)^ instead of \Delta). It appears in connection to an "error term" involved in counting the number of ways of expressing an integer as a sum of 24 squares. A formula due to Ian G. Macdonald was given in . Values The first few values of the tau function are given in the following table : Calculating this function on an odd square number (i.e. a centered octagonal number) yields an odd number, whereas for any other number the function yields an even number. Ramanujan's conjectures observed, but did not prove, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Time
In relativity, proper time (from Latin, meaning ''own time'') along a timelike world line is defined as the time as measured by a clock following that line. The proper time interval between two events on a world line is the change in proper time, which is independent of coordinates, and is a Lorentz scalar. The interval is the quantity of interest, since proper time itself is fixed only up to an arbitrary additive constant, namely the setting of the clock at some event along the world line. The proper time interval between two events depends not only on the events, but also the world line connecting them, and hence on the motion of the clock between the events. It is expressed as an integral over the world line (analogous to arc length in Euclidean space). An accelerated clock will measure a smaller elapsed time between two events than that measured by a non-accelerated ( inertial) clock between the same two events. The twin paradox is an example of this effect. By conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kendall Tau Rank Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the Kendall rank correlation coefficient, commonly referred to as Kendall's τ coefficient (after the Greek letter τ, tau), is a statistic used to measure the ordinal association between two measured quantities. A τ test is a non-parametric hypothesis test for statistical dependence based on the τ coefficient. It is a measure of rank correlation: the similarity of the orderings of the data when ranked by each of the quantities. It is named after Maurice Kendall, who developed it in 1938, though Gustav Fechner had proposed a similar measure in the context of time series in 1897. Intuitively, the Kendall correlation between two variables will be high when observations have a similar (or identical for a correlation of 1) rank (i.e. relative position label of the observations within the variable: 1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc.) between the two variables, and low when observations have a dissimilar (or fully different for a correlation of −1) rank between the two variab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stopping Time
In probability theory, in particular in the study of stochastic processes, a stopping time (also Markov time, Markov moment, optional stopping time or optional time ) is a specific type of "random time": a random variable whose value is interpreted as the time at which a given stochastic process exhibits a certain behavior of interest. A stopping time is often defined by a stopping rule, a mechanism for deciding whether to continue or stop a process on the basis of the present position and past events, and which will almost always lead to a decision to stop at some finite time. Stopping times occur in decision theory, and the optional stopping theorem is an important result in this context. Stopping times are also frequently applied in mathematical proofs to "tame the continuum of time", as Chung put it in his book (1982). Definition Discrete time Let \tau be a random variable, which is defined on the filtered probability space (\Omega, \mathcal F, (\mathcal F_n)_, P) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse over time and can result in dementia. Most documented cases have occurred in athletes involved in striking-based combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, mixed martial arts, and contact sports such as rugby union, rugby league, American football, Australian rules football, professional wrestling, and ice hockey. It is also an issue in association football (soccer), but largely as a result of heading the ball rather than player contact. Other risk factors include being in the military ( combat arms), prior domestic violence, and repeated banging of the head. The exact amount of trauma required for the condition to occur is unknown, and as of 2025 definitive diagnosis can only occur at autopsy. The disease is classified as a tauop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is a pathological process that occurs in frontotemporal dementia. It is characterized by atrophy in the frontal lobe and temporal lobe of the brain, with sparing of the parietal and occipital lobes. Common proteinopathies that are found in FTLD include the accumulation of tau proteins and TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43). Mutations in the '' C9orf72'' gene have been established as a major genetic contribution of FTLD, although defects in the granulin (GRN) and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are also associated with it. Classification There are 3 main histological subtypes found at post-mortem: * FTLD-tau is characterised by tau positive inclusion bodies often referred to as Pick-bodies. Examples of FTLD-tau include; Pick's disease, corticobasal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy. * FTLD-TDP (or FTLD-U ) is characterised by ubiquitin and TDP-43 positive, tau negative, FUS negative inclusion bodies. The pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific substance after administration. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is based on mathematical modeling that places great emphasis on the relationship between drug plasma concentration and the time elapsed since the drug's administration. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects the drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress or force per unit area is: \tau = ,where is the force applied and is the cross-sectional area. The area involved corresponds to the material face (geometry), face parallel to the applied force vector, i.e., with surface normal vector perpendicular to the force. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as:\tau_w := \mu\left.\frac\_,where is the dynamic viscosity, is the flow velocity, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |